The four point electrical probe is a very versatile device used widely in physics for the investigation of electrical phenomena. Colorado Superconductor Inc. has especially designed two four point superconducting devices from the YBa2Cu3O7 and the Bi2Sr2Ca2Cu3O10 materials for such investigations. The Complete Exploration Kit and the Super Exploration Kit contain four point electrical probes.
When a simple measurement of the electrical resistance of a test sample is performed by attaching two wires to it, one inadvertently also measures the resistance of the contact point of the wires to the sample. Typically the resistance of the point of contact (called contact resistance) is far smaller than the resistance of the sample, and can thus be ignored. However, when one is measuring a very small sample resistance, especially under variable temperature conditions, the contact resistance can dominate and completely obscure changes in the resistance of the sample itself. This is the situation that exists for superconductors.
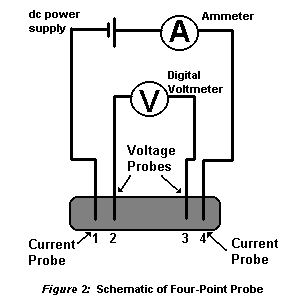
The effects of contact resistance can be eliminated with the use of a four point probe. A schematic of a four point probe is shown in figure 2 below. In this diagram, four wires (or probes) have been attached to the test sample. A constant current is made to flow the length of the sample through probes labeled 1 and 4 in the figure. This can be done using a current source or a power supply as shown. Many power supplies have a current output readout built into them. If not, an ammeter in series with this circuit can be used to obtain the value of the current. A 5 Watt power supply capable of producing up to 0.5 Amp is required for the experiments described for our superconducting devices.
If the sample has any resistance to the flow of electrical current, then there will be a drop of potential (or voltage) as the current flows along the sample, for example between the two wires (or probes) labeled 2 and 3 in the figure. The voltage drop between probes 2 and 3 can be measured by a digital voltmeter. The resistance of the sample between probes 2 and 3 is the ratio of the voltage registering on the digital voltmeter to the value of the output current of the power supply. The high impedance of the digital voltmeter minimizes the current flow through the portion of the circuit comprising the voltmeter. Thus, since there is no potential drop across the contact resistance associated with probes 2 and 3, only the resistance associated with the superconductor between probes 2 and 3 is measured.
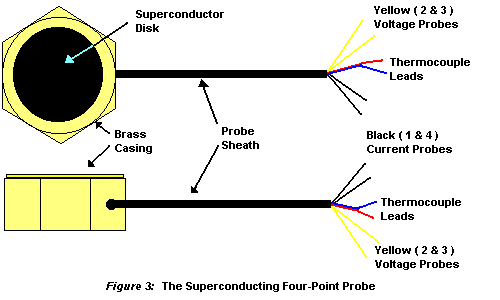
The four point probe devices in the Complete Exploration Kit and the Super Exploration Kit are both encapsulated in rugged brass casings. On one side of the casing, the superconductor disk is visible. An aluminum end cap has been inserted on the back side of the brass casing to seal and to protect the probe connections with the superconductor. Please do not attempt to remove the end cap. A matched thermocouple has also been attached to the superconductor in this casing. This thermocouple is a type 'T'.
The Bi2Sr2Ca2Cu3O10 superconductor four point electrical probe casing is larger than the YBa2Cu3O7 casing. The aluminum backs of the probes have either BSCCO, or YBCO printed on them, for further identification.
The illustration in figure 3 below, shows the salient features of the four point probe devices. The pair of black wires are current leads for the input of current from the power supply, and have been labeled probes 1 and 4 in figure 2. The pair of yellow wires are the voltage measurement probes for measuring the voltage drop across the superconductor with the help of a digital voltmeter, and have been labeled probes 2 and 3 in figure 2. The red and blue wires are leads for the thermocouple.
Information Courtesy of CSI Superconductors

