The navigation PC Board may be used to make a visual, mobile robot, or a PC based digital compass.

The digital navigation PC board may be configured for a number of navigation functions, see figure 1. It may be made into a simple visual digital compass, or a microcontroller based compass. The microcontroller based compass can be used for mobile robotics or a PC based compass.
1490 Digital Compass
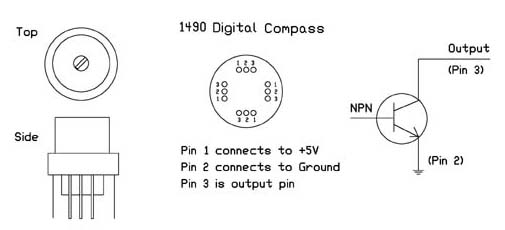
The sensor used on the PC Board is the 1490 digital compass manufactured by Robson Company, see figure 2. This sensor is a solid-state Hall effect device. It is sensitive enough to detect the Earth's weak magnetic field. When rotated it can display the position of the four cardinal points on a compass, North (N), South (S), East (E) and West (W). As well as the intermediate directions: North East (NE), North West (NW), South East (SE), and South West (SW), see figure 3.

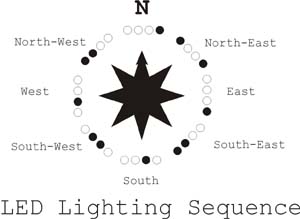
The sensor is dampened to approximate the speed of a liquid filled compass. The dampening prevents over swinging the direction. In addition the built in hysteresis prevents flutter when near a switching direction. The 1490 device is sensitive to tilt. Any tilt greater than 12 degrees will create directional errors.
The bottom of the device has 12 leads arranged in four groups of three leads. Looking at the device from the top each group of leads are labeled 1, 2 and 3. The leads labeled 1 are connected to Vcc (+5V). Leads numbered 2 are connected to ground. And the leads labeled 3 are our output leads. The output leads of the device are equivalent to an open collector of an NPN transistor, see figure 4. Each output is capable of sinking 20 mA continuously or up to 25 mA intermittently.